Difference between revisions of "Conscription"
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Caricature-1780-press_gang.jpg|thumb|Depiction of a [[Royal Navy]] [[press gang]], 1780.]] |
[[File:Caricature-1780-press_gang.jpg|thumb|Depiction of a [[Royal Navy]] [[press gang]], 1780.]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:GKVi3e-WQAArpIX.jpeg|thumb|[[Meme]] advocating for equality in conscription.]] |
||
[[Conscription]] (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. With few exceptions conscription applies exclusively to men. |
[[Conscription]] (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. With few exceptions conscription applies exclusively to men. |
||
| Line 5: | Line 7: | ||
Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1–8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force. |
Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1–8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force. |
||
| − | Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived violation of individual rights. Those conscripted may evade service, sometimes by leaving the country, |
+ | Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived violation of individual rights. Those conscripted may evade service, sometimes by leaving the country, and seeking asylum in another country. Some selection systems accommodate these attitudes by providing alternative service outside combat-operations roles or even outside the military, such as Siviilipalvelus (alternative civil service) in Finland, Zivildienst (compulsory community service) in Austria, Germany and Switzerland. Several countries conscript male soldiers not only for armed forces, but also for paramilitary agencies, which are dedicated to police-like domestic only service like internal troops, border guards or non-combat rescue duties like civil defence. |
| − | As of 2022, many states no longer conscript soldiers, relying instead upon professional militaries with volunteers. The ability to rely on such an arrangement, however, presupposes some degree of predictability with regard to both war-fighting requirements and the scope of hostilities. Many states that have abolished conscription still, therefore, reserve the power to resume conscription during wartime or times of crisis. |
+ | As of 2022, many states no longer conscript soldiers, relying instead upon professional militaries with volunteers. The ability to rely on such an arrangement, however, presupposes some degree of predictability with regard to both war-fighting requirements and the scope of hostilities. Many states that have abolished conscription still, therefore, reserve the power to resume conscription during wartime or times of crisis. States involved in wars or interstate rivalries are most likely to implement conscription, and democracies are less likely than autocracies to implement conscription. With a few exceptions, such as Singapore and Egypt, former British colonies are less likely to have conscription, as they are influenced by British anti-conscription norms that can be traced back to the English Civil War; the United Kingdom abolished conscription in 1960. |
* http://womenalliance.org/no-to-female-conscription |
* http://womenalliance.org/no-to-female-conscription |
||
* https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202001/22/WS5e27a9f7a310128217272b2b.html |
* https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/a/202001/22/WS5e27a9f7a310128217272b2b.html |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Feminism == |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2024-04-15-135423_597x133_scrot.png|400px]] |
||
| + | |||
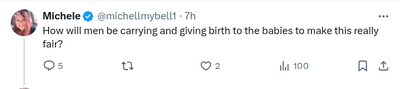
| + | Feminists sometimes argue women should not be conscripted because they are needed to produced children. This argument is at odds with other feminist arguments and the birthrate in Western nations.<ref>https://twitter.com/michellmybell1/status/1779600355900150088</ref><ref>https://archive.is/wip/LUtB7</ref> |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Table == |
||
{| class="sortable wikitable" |
{| class="sortable wikitable" |
||
| Line 30: | Line 40: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|Angola |
|Angola |
||
| + | |20-45 |
||
| + | |24 |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Argentina |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 35: | Line 51: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Armenia |
||
| + | |18-27 |
||
| + | |24 |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Austria |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 41: | Line 63: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Azerbaijan |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 47: | Line 69: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Belarus |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 53: | Line 75: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Belize |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 59: | Line 81: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Benin |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 65: | Line 87: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Bhutan |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 71: | Line 93: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Bolivia |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 77: | Line 99: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Brazil |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 83: | Line 105: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Cambodia |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 89: | Line 111: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Cape Verde |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 95: | Line 117: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Chad |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 101: | Line 123: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Chile |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 107: | Line 129: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |China |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 113: | Line 135: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Colombia |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 119: | Line 141: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Congo |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 125: | Line 147: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Cuba |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 131: | Line 153: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Cyprus |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 137: | Line 159: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Denmark |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 143: | Line 165: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Egypt |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 149: | Line 171: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |El Salvador |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 155: | Line 177: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Equatorial Guinea |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 161: | Line 183: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Eritrea |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 167: | Line 189: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Estonia |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 173: | Line 195: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Ethiopia |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| − | | |
||
| − | |- |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Finland |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 186: | Line 207: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Georgia |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 192: | Line 213: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Greece |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 198: | Line 219: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Guatamala |
||
| − | |||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 205: | Line 225: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Guinea-Bissau |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 211: | Line 231: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Indonesia |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 217: | Line 237: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Iran |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 223: | Line 243: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Israel |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 229: | Line 249: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Ivory Coast |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 235: | Line 255: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Jordan |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 241: | Line 261: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Kazakhstan |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 247: | Line 267: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Kuwait |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| − | | |
||
| − | |- |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Kyrgystan |
||
| − | | |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 260: | Line 279: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Laos |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Lithuania |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 266: | Line 291: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Mali |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Mexico |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 272: | Line 303: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Moldova |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Mongolia |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 278: | Line 315: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Moroco |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Mozanbique |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 284: | Line 327: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Myanmar |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Niger |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 290: | Line 339: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |North Korea |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Norway |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 296: | Line 351: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Paraguay |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Poland |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 302: | Line 363: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Portugal |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Qatar |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 308: | Line 375: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Russia |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |San Marino |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 314: | Line 387: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |San Tome and Principe |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Senegal |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 320: | Line 399: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Singapore |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Slovakia |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 326: | Line 411: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Somalia |
||
| − | |- |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |South Korea |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 333: | Line 423: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |South Sudan |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Spain |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 339: | Line 435: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Sudan |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Sweden |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 345: | Line 447: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Switzerland |
||
| − | |- |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Syria |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 352: | Line 459: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Taiwan |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Tajikistan |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 358: | Line 471: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Thailand |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Timor-Leste |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 364: | Line 483: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Tunisia |
||
| − | |- |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Turkey |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 371: | Line 495: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Turkmenistan |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Ukraine |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 377: | Line 507: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |United Arab Emirate |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| − | ||- |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |United States |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 387: | Line 519: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Uruguay |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Uzbekistan |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 393: | Line 531: | ||
| |
| |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| + | |Venezuela |
||
| |
| |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | | |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Vietnam |
||
| |
| |
||
| |
| |
||
| Line 415: | Line 559: | ||
{{Conscription}} |
{{Conscription}} |
||
| + | {{Draft}} |
||
{{Gynocentrism}} |
{{Gynocentrism}} |
||
{{Wikipedia}} |
{{Wikipedia}} |
||
Latest revision as of 03:58, 15 April 2024

Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. With few exceptions conscription applies exclusively to men.
Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1–8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force.
Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived violation of individual rights. Those conscripted may evade service, sometimes by leaving the country, and seeking asylum in another country. Some selection systems accommodate these attitudes by providing alternative service outside combat-operations roles or even outside the military, such as Siviilipalvelus (alternative civil service) in Finland, Zivildienst (compulsory community service) in Austria, Germany and Switzerland. Several countries conscript male soldiers not only for armed forces, but also for paramilitary agencies, which are dedicated to police-like domestic only service like internal troops, border guards or non-combat rescue duties like civil defence.
As of 2022, many states no longer conscript soldiers, relying instead upon professional militaries with volunteers. The ability to rely on such an arrangement, however, presupposes some degree of predictability with regard to both war-fighting requirements and the scope of hostilities. Many states that have abolished conscription still, therefore, reserve the power to resume conscription during wartime or times of crisis. States involved in wars or interstate rivalries are most likely to implement conscription, and democracies are less likely than autocracies to implement conscription. With a few exceptions, such as Singapore and Egypt, former British colonies are less likely to have conscription, as they are influenced by British anti-conscription norms that can be traced back to the English Civil War; the United Kingdom abolished conscription in 1960.
Feminism
Feminists sometimes argue women should not be conscripted because they are needed to produced children. This argument is at odds with other feminist arguments and the birthrate in Western nations.[1][2]
Table
| Country | Men | Women | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Range | Duration (months) | Age Range | Duration (months) | |
| Algeria | 19-30 | 12 | ||
| Angola | 20-45 | 24 | ||
| Argentina | ||||
| Armenia | 18-27 | 24 | ||
| Austria | ||||
| Azerbaijan | ||||
| Belarus | ||||
| Belize | ||||
| Benin | ||||
| Bhutan | ||||
| Bolivia | ||||
| Brazil | ||||
| Cambodia | ||||
| Cape Verde | ||||
| Chad | ||||
| Chile | ||||
| China | ||||
| Colombia | ||||
| Congo | ||||
| Cuba | ||||
| Cyprus | ||||
| Denmark | ||||
| Egypt | ||||
| El Salvador | ||||
| Equatorial Guinea | ||||
| Eritrea | ||||
| Estonia | ||||
| Ethiopia | ||||
| Finland | ||||
| Georgia | ||||
| Greece | ||||
| Guatamala | ||||
| Guinea-Bissau | ||||
| Indonesia | ||||
| Iran | ||||
| Israel | ||||
| Ivory Coast | ||||
| Jordan | ||||
| Kazakhstan | ||||
| Kuwait | ||||
| Kyrgystan | ||||
| Laos | ||||
| Lithuania | ||||
| Mali | ||||
| Mexico | ||||
| Moldova | ||||
| Mongolia | ||||
| Moroco | ||||
| Mozanbique | ||||
| Myanmar | ||||
| Niger | ||||
| North Korea | ||||
| Norway | ||||
| Paraguay | ||||
| Poland | ||||
| Portugal | ||||
| Qatar | ||||
| Russia | ||||
| San Marino | ||||
| San Tome and Principe | ||||
| Senegal | ||||
| Singapore | ||||
| Slovakia | ||||
| Somalia | ||||
| South Korea | ||||
| South Sudan | ||||
| Spain | ||||
| Sudan | ||||
| Sweden | ||||
| Switzerland | ||||
| Syria | ||||
| Taiwan | ||||
| Tajikistan | ||||
| Thailand | ||||
| Timor-Leste | ||||
| Tunisia | ||||
| Turkey | ||||
| Turkmenistan | ||||
| Ukraine | ||||
| United Arab Emirate | ||||
| United States | ||||
| Uruguay | ||||
| Uzbekistan | ||||
| Venezuela | ||||
| Vietnam | ||||
See Also
External Links
References
This is a draft article and so will not be published on A Voice for Men or appear in random article selections. Wiki4Men is looking for trustworthy editors that can turn draft articles in to featured articles. Information on how to apply is on the Main Page.
This article contains information imported from the English Wikipedia. In most cases the page history will have details. If you need information on the importation and have difficulty obtaining it please contact the site administrators.
Wikipedia shows a strong woke bias. Text copied over from Wikipedia can be corrected and improved.