Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
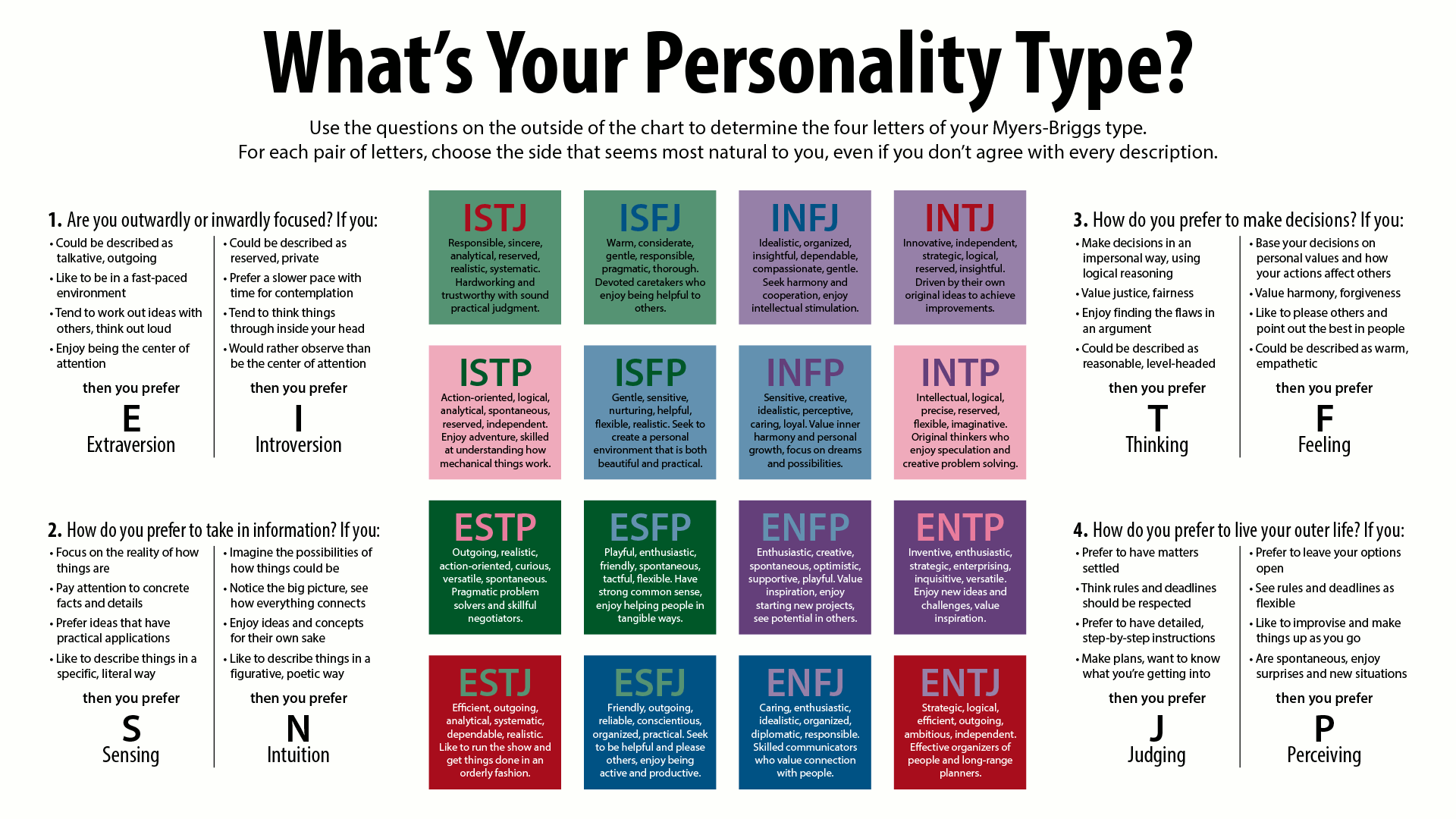
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a self-report questionnaire that indicates differing psychological types, which are often commonly called personality types. The test assigns a binary value to each of four categories:
- Introversion or Extraversion
- Sensing or Intuition
- Thinking or Feeling
- Judging or Perceiving
One letter from each category is taken to produce a four-letter test result representing one of sixteen possible types, such as "INTP" or "ESFJ".
As a self-reporting questionaire the results are only as good as the truthfulness of the answers provided.
The MBTI was constructed by two Americans: Katharine Cook Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs Myers, who were inspired by the book Psychological Types by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung. Isabel Myers was particularly fascinated by the concept of introversion and she typed herself as an "INFP". However, she felt the book was too complex for the general public, and therefore she tried to organize the Jungian cognitive functions to make it more accessible.
Wikipedia is highly critical of MBTI. Since 10 February 2024, and still as of 26 December 2025, Wikipedia openly calls MBTI pseudoscientific.[1][2]
Tables
The data below is drawn from the MBTI Manual produced by CPP.[3][4]
The ratio in the table below is a signed ratio. If males outnumber females by type the value is positive, otherwise it is negative. No types have a ratio of 1.0.
Types
MBTI categories vary substantially with gender. It is also notable that most women cluster in to a smaller number of categories, which is consistent with male variability.
| Type | Gender | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Ratio | |
| ENFJ | 1.6% | 3.3% | -2.06 |
| ENFP | 6.4% | 9.7% | -1.52 |
| ENTJ | 2.7% | 0.9% | +3.0 |
| ENTP | 4.0% | 2.4% | +1.67 |
| ESFJ | 7.5% | 16.9% | -2.25 |
| ESFP | 6.9% | 10.1% | -1.46 |
| ESTJ | 11.2% | 6.3% | +1.78 |
| ESTP | 5.6% | 3.0% | +1.87 |
| INFJ | 1.2% | 1.6% | -1.33 |
| INFP | 4.1% | 4.6% | -1.12 |
| INTJ | 3.3% | 0.9% | +3.67 |
| INTP | 4.8% | 1.7% | +2.82 |
| ISFJ | 8.1% | 19.4% | -2.40 |
| ISFP | 7.6% | 9.9% | -1.30 |
| ISTJ | 16.4% | 6.9% | +2.38 |
| ISTP | 8.5% | 2.3% | +3.70 |
Process Pairs
The middle two types combined are now termed as process pairs.[5][6]
| Process Pairs | Gender | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Ratio | |
| NF | 13.3% | 19.2% | -1.4436 |
| NT | 14.8% | 5.9% | +2.5085 |
| SF | 30.1% | 56.3% | -1.8704 |
| ST | 41.7% | 18.5% | +2.2541 |
Preferences
| Preference | Gender | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Ratio | |
| Extraversion (E) | 45.9% | 52.6% | -1.1460 |
| Feeling (F) | 43.4% | 75.5% | -1.7396 |
| Introversion (I) | 54.0% | 47.3% | +1.1416 |
| Intuition (N) | 28.1% | 25.1% | +1.1195 |
| Judging (J) | 52.0% | 56.2% | -1.0808 |
| Perceiving (P) | 47.9% | 43.8% | +1.0936 |
| Sensing (S) | 71.8% | 74.8% | -1.0418 |
| Thinking (T) | 56.5% | 24.4% | +2.3156 |
Wikipedia
This article contains information imported from the English Wikipedia. In most cases the page history will have details. If you need information on the importation and have difficulty obtaining it please contact the site administrators.
Wikipedia shows a strong woke bias. Text copied over from Wikipedia can be corrected and improved.
References
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Myers%E2%80%93Briggs_Type_Indicator&oldid=1243217039
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Myers%E2%80%93Briggs_Type_Indicator&oldid=1328670335
- ↑ https://www.careerplanner.com/MB2/TypeInPopulation-Males-Females.cfm
- ↑ https://archive.is/j3K0e
- ↑ https://www.myersbriggs.org/unique-features-of-myers-briggs/type-dynamics-overview/
- ↑ https://archive.is/wip/8gT1E